In nature nothing happens without a reason. Every substance is made up of atoms and molecules. There was a time when it was assumed that atom is the smallest part of a substance and it cannot be broken. With the progress of science we have come to know that each atom has three subatomic particles named electron, proton and neutron. The electron is negatively charged and the protons are positively charged. When an atom loses the negatively charged electrons it becomes positively charged and when new electrons enter an atom it becomes negatively charged.
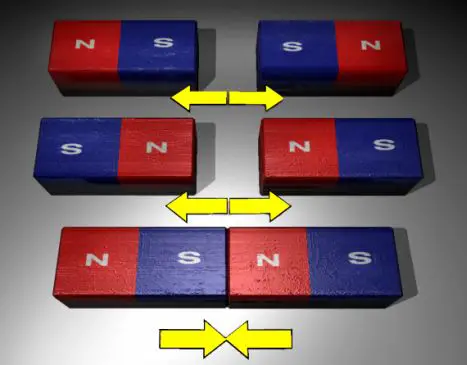
Opposite poles of a magnet attract each other but if two same poles are brought closer they repel each other. We can visually perceive this natural phenomenon. The magnets have magnetic field around them and they can attract some neutral substances like nickel, iron and steel. The fact is that every magnet has two poles- North Pole and South Pole. At one pole the negatively charged particles or electrons tend to gather and at the opposite end there is a dearth of electrons. The presence of the electrons affects the attraction or repulsion force acting between the poles.
The protons and electrons have electric fields around them and it helps them attract the opposite charge but the electric field around similar charges repels each other. The like charges repel each other following the third law of Newton, according to which every action has an opposite yet equal reaction. The attraction or repulsion forces acting between two charges are always of the same magnitude and act in opposite directions. When a negatively charged object is brought closer to a neutral object the protons get attracted towards them but the electrons get repelled and move to the opposite side. This way the neutral object gets divided into two poles- one positively charged and another negatively charged.